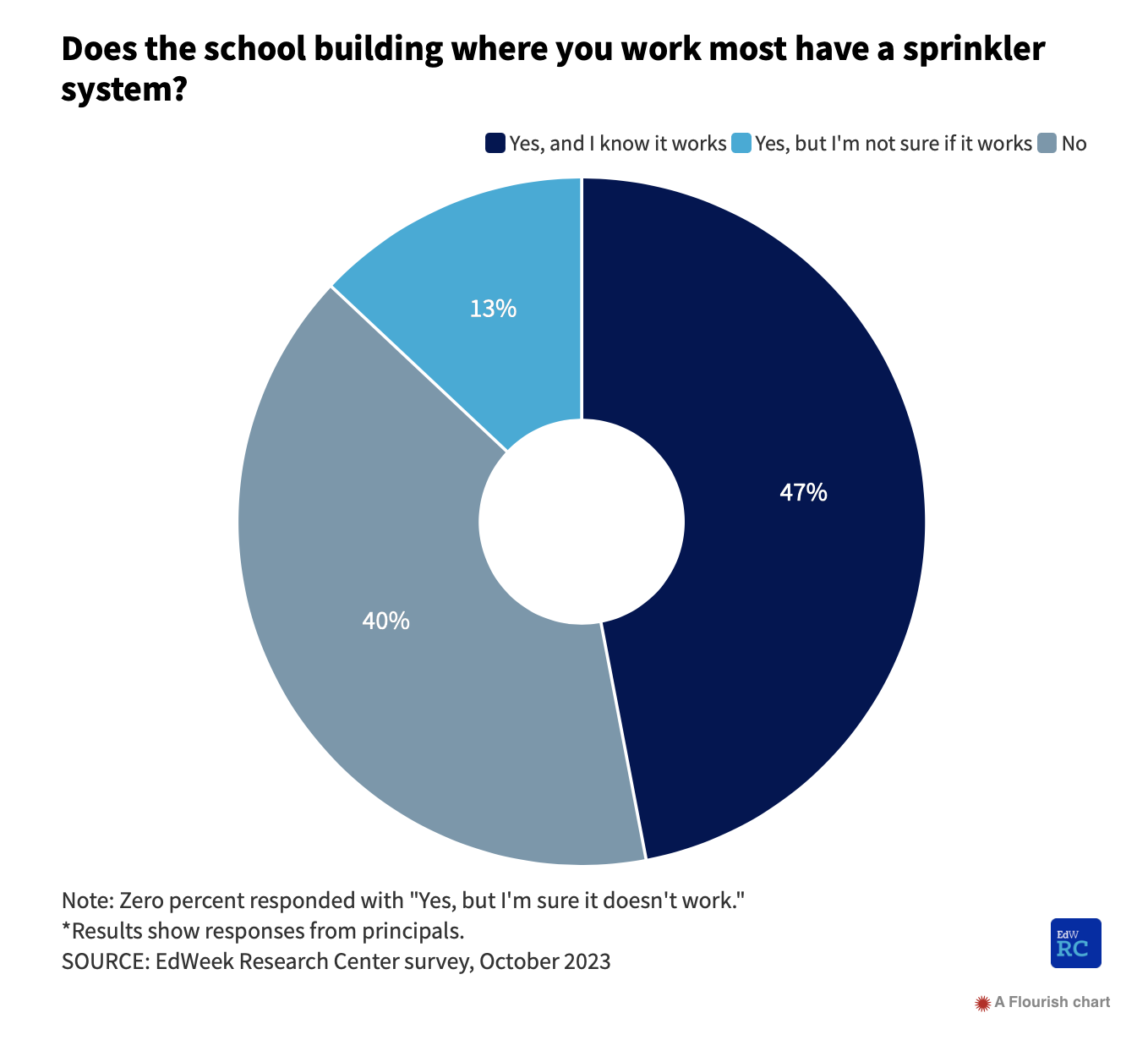
A survey conducted in the fall by the Education Week Research Center asked school principals whether the building where they most often work has working sprinklers.
- Two out of five said no, meaning tens of thousands of school buildings are missing fire control tools.
- Moreover, 13% said they’re not sure whether the currently installed sprinklers in their buildings work.
The quality and effectiveness of fire sprinkler systems in schools can vary widely based on such factors as the age of the school building, local building codes and renovations or updates made over time. While there are strict regulations and building codes that mandate the installation of fire sprinklers in new school construction, many older school buildings may not have such systems—and research points to the fact that taxpayers are not willing to raise taxes to address these needs.
In a concerted effort to bolster safety measures in educational institutions, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) updated NFPA 101, the Life Safety Code, specifically tailored to address the unique needs of schools across the United States. The NFPA 101 is a comprehensive set of regulations designed to ensure the safety of occupants in various structures, including schools. The latest revisions come as a response to the evolving landscape of safety concerns within educational facilities.
Here are key points related to NFPA 101 for schools:
Emergency Egress:
- Specifies requirements for safe and efficient means of egress during emergencies.
- Addresses design and maintenance of exit routes, exit doors and exit signage.
Fire Protection:
- Outlines measures for fire prevention and protection within school buildings.
- Covers fire detection, alarm systems and suppression equipment.
Building Construction and Renovation:
- Provides guidelines for the construction and renovation of school buildings to enhance safety.
- Addresses materials, structural integrity and fire-resistant features.
Accessibility and Evacuation:
- Ensures accessibility for individuals with disabilities during normal and emergency conditions.
- Specifies requirements for evacuation procedures, including plans for persons with special needs.
Occupancy Classification:
- Defines different areas within schools and assigns appropriate safety measures based on occupancy classification.
- Addresses unique requirements for classrooms, assembly areas, laboratories and other spaces.
Maintenance of Systems:
- Emphasizes the importance of regular maintenance for life safety systems, such as fire alarms and sprinklers.
- Ensures that systems are in good working order to respond effectively during emergencies.
Means of Egress Illumination:
- Specifies requirements for lighting along exit paths and signage to ensure visibility during emergencies.
- Addresses emergency lighting and power sources.
Fire Drills and Emergency Preparedness:
- Outlines the frequency and procedures for conducting fire drills in schools.
- Emphasizes the importance of emergency preparedness plans for school staff and students.
Special Hazards:
- Identifies and addresses special hazards that may be present in school environments.
- Provides guidelines for handling hazardous materials, equipment or processes.
Security Measures:
- Recommends security measures to prevent unauthorized access and enhance overall safety.
- Addresses issues related to crime prevention and emergency response coordination.
It's important to note that NFPA 101 is periodically updated, and users should refer to the latest edition for the most current information and compliance requirements. Additionally, local building and fire codes also may apply.

